Our jaws have evolved in such a way which does not allow sufficient space for the eruption of a third set of molars, also known as wisdom teeth.
As a result of this, wisdom teeth can often cause problems for many people. These problems include food impaction, pain, decay, swelling in the region of the wisdom tooth and infection. If this is the case, their removal may be indicated.
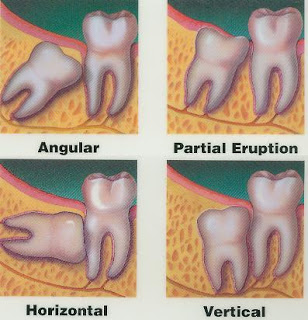 Often, wisdom teeth may be impacted and require removal. Impacted teeth are generally more likely to cause problems. Impaction means that the wisdom teeth will not grow or erupt into a position that allows them to be functional. Impaction may be due to soft tissues (gums) or hard tissues (other teeth or bone). If your wisdom teeth have not erupted fully and are covered partially by your gums and you are older than 17 or 18 years old then your wisdom teeth are likely to be impacted.
Often, wisdom teeth may be impacted and require removal. Impacted teeth are generally more likely to cause problems. Impaction means that the wisdom teeth will not grow or erupt into a position that allows them to be functional. Impaction may be due to soft tissues (gums) or hard tissues (other teeth or bone). If your wisdom teeth have not erupted fully and are covered partially by your gums and you are older than 17 or 18 years old then your wisdom teeth are likely to be impacted.
Some people elect to wait until they are experiencing pain before considering removal of their wisdom teeth. The trouble with this is that sometimes the damage caused by wisdom teeth may proceed in this time without any warning. Problematic wisdom teeth are best removed as soon as possible. Recovery time for younger patients is much shorter than for older patients. Research has demonstrated that patients who are older than 24 years old when they elect to have their wisdom teeth removed are more likely to suffer from more complications from them. Pain with wisdom teeth can strike at any time which is why it is a good idea to be proactive and arrange for the removal of the wisdom teeth as soon as there are signs that they may require removal. As a general rule, your wisdom teeth will become more difficult to remove the older you are.
For anxious patients, IV sedation or "twilight sedation" may be an option. To read more about twilight sedation you can visit our page on Sedation. Some wisdom teeth removals are best done at a hospital under a general anaesthetic.
When there is adequate space in your jaws, wisdom teeth can erupt into the mouth in the correct position for chewing and cleaning. In this case, their removal would not be required.
The dentist will assess these teeth, based on a clinical examination and diagnostic xrays, and let you know if they require removal. Removal of wisdom teeth can be challenging and often require referral to a specialist oral surgeon for management.
To read even more about wisdom teeth, visit our news item Wising up about wisdom teeth.
